Emotion measurement (or facial expression analysis) is a technology tracking people’s emotions. It delivers deep qualitative insights into customers’ reactions and sentiments which significantly influence their purchase decisions. Emotion measurement helps to better understand how customers engage with marketing products and communications, as well as with all other forms of visual content.
Insights organizations have used human observations of recorded videos to try to assess emotional responses for many years. Historically, these tools have been expensive and oftentimes required a physical location (lab) to administer these tests.
CoolTool has advanced these tools, previously used in laboratory settings, to enable remote applications that are device agnostic. This enables marketers, brand managers, insights firms, content creators, and companies of all sizes to use this fast and affordable technique to capture a much more holistic view of consumer behavioral and nonconscious reactions to visual marketing products, communications, and various forms of content.

According to research by Dr. Paul Ekman, a pioneer in the study of emotions and facial expressions and Professor Emeritus of Psychology at the University of California Medical School, brief flashes of emotion displayed on the respondent’s face – or “micro-expressions” – reveal a person’s beliefs and their propensity to act or buy.
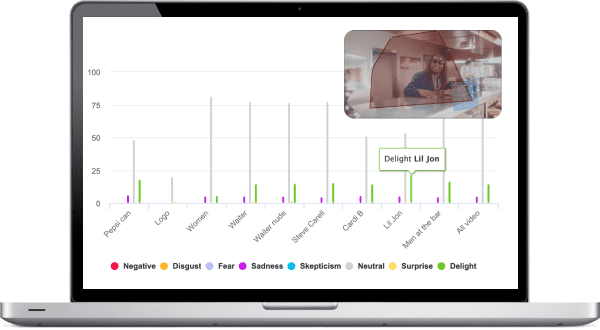
CoolTool’s online facial coding technology uses the built-in cameras of desktops, laptops, tablets, and mobile devices. It captures such micro-expressions, automatically decodes them and transforms into data and visualized reporting. We define seven facial expressions - happiness, surprise, fear, negative, disgust, sadness, and skepticism. Each emotion can be recognized independent of age, race, and gender.
Compared to traditional research methods, where respondents may not be able to articulate their true attitudes, emotion measurement is far more reliable and accurate as it eliminates the so-called “human factor” bias.
The primary use case for those researchers implementing emotional measurement is with various forms of video, including ads, promotions, how-to’s, TV/movie trailers, vlog posts, etc. Within a survey, an advertisement can be shown during which the respondent’s device camera will record their reactions. Traditionally, respondents would answer questions about the advertisement, rating it on various scales. In most cases, results are dependent on the respondent’s ability to recall what they’ve just been shown, their interpretation of their own emotions, and their ability to put those emotions into words.
Using technology that monitors facial expressions bypasses these issues by capturing data as the respondent views a video. It enables advertisers to understand how the tiniest elements of their video may impact audience response.
The result? An unprecedented level of insight into what affects customer emotions. Such valuable information can drive better business decisions, resulting in improved products and service offerings and experiences.
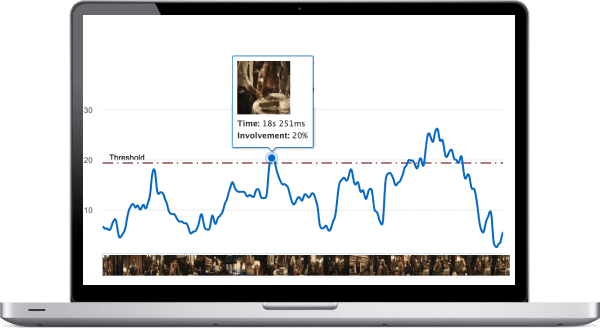
Emotion measurement technology help researchers address the challenges they are facing:
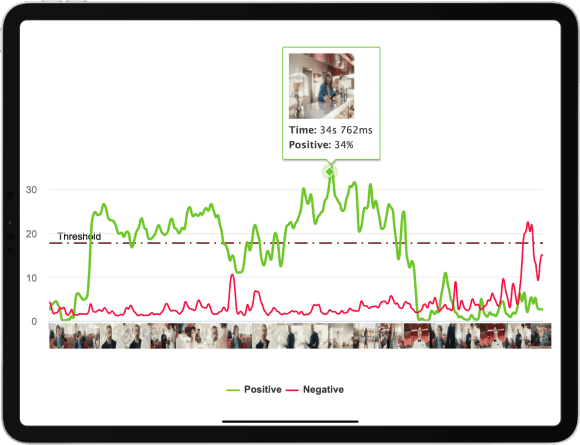
- A higher speed of data analysis and processing
- More accurate results of data analysis and better quality of insights
- Reduction of research time and human-resource-related expenses
- Exclusion of human factor of social bias in survey responses
- Reduction in interpretation errors related to traditional survey answers
- Application of additional technologies (eye-tracking for example), allows understanding which emotion a particular object provoked

